At the time of this post, WA Health has been funded for the next three years to write the specifications and choose a vendor to develop an Electronic Medical Record, or EMR. This will be a statewide EMR for WA Health’s public hospitals and health services. From January to June 2024 HCC has been working with our EMR Consumer Reference Group to up-skill ourselves on all things digital, so we are able to provide the consumer voice into this part of the process. In March 2024 we convened a webinar entitled Can the EMR stitch up our health system? This blog has links to the replay, transcripts and summary and provides insights into what consumers need to think about. Consumer involvement in WA’s EMR is being funded by WA Health to ensure a strong consumer voice. WA has been leading the nation in the level of consumer involvement in this important initiative.
This blog series has been written by Pip Brennan who is working for HCC on the project, co-located in the Health Department.
Interoperability is just a fancy word for your health information following you, from GP to hospital, allied provider to pharmacist to specialist and back again. In 2021, HCC co-designed an Electronic Medical Record Consumer Charter which has this to say about interoperability:
- Accuracy: My health records are complete, accurate and up to date.
- Equitable care: My health records are available to my treating clinicians regardless of where I am being treated.
- Transparency, Choice and Control: I have access to my real-time health information at no cost to me or my family.
I’m just pausing for a moment to remind people of the difference between an Electronic Medical Record and My Health Record. The dot points from the Charter above refer to WA’s future Electronic Medical Record. The Electronic Medical Record and My Health Record are different as per the image below. An Electronic Medical Record is based within a hospital or health service. My Health Record contains federally based information such as GP care and immunisation records. We want the two to talk to each other. That is interoperability.

Australia is doing a significant amount of work on interoperability at a national level. We now have a National Healthcare Interoperability Plan, and this potentially offers WA an opportunity to have a more joined-up EMR than other states and territories who developed their EMRs prior to this policy coming into being.
There’s a change in the air that as if to say everyone recognises that we have an opportunity, probably a once in not just a single generation, but multi generation opportunity to fundamentally transform the way our health system works
Harry Iles Mann
Webinar – Can an EMR stitch up our health system?
Because of all the work happening nationally, we invited National Consumer Leader and Digital Health Expert Harry Iles Mann to talk with WA’s Chief Clinical Information Officer Dr Peter Sprivulis about WA’s Electronic Medical Record and how that could connect up our health care.
You can read the whole transcript, or highlights here, or watch the whole replay here.
Key messages about interoperability:
- It’s all about culture. The technology is the easy bit. It’s the culture that is the difficult aspect to digital health transformation.
- Get workflows right. Ensure that the words mean the same on each side of the transaction – that GPs and hospital staff mean the same thing. e.g. allergies.
- Legal and regulatory levels. There is potential for the My Health Record Act to be broadened to become My Health Information Act. This will provide a safety for health consumers, and puts very clear obligations on health services to share data appropriately. This is a long term reform.
- Financial and cultural piece – we need to deal with perverse incentives to make the right thing the easy thing for clinicians. For example, currently if a GP speaks to a specialist about a patient, neither is compensated, even though this could expedite care for a patient and avoid unnecessary, inconvenient, costly consultations. There needs to be a joined-up conversation with private, public, state and federal health to sort this out.
- My Health Record is still key – There is ongoing investment in the My Health Record as a platform to facilitate interoperability and consumer access to their information. Yes, My Health Record has its issues – but a key reason for the ongoing investment is that regardless of what states and territories or different vendors do in developing EMRs, there will be something that is sitting within the custodianship of government that is a point of access for you and your health information.
- We’ve made a start – WA has digitised parts of the Electronic Medical Records in WA’s hospitals, but this will see us take a bit leap forward. An EMR is all about the bedside workflows – this is where all the risk sits.
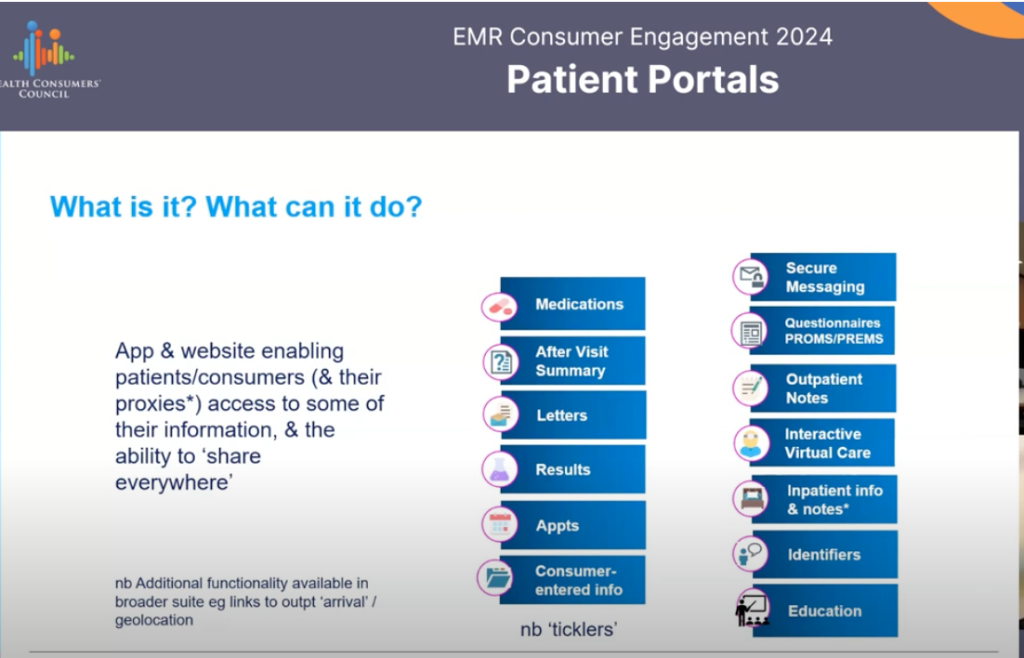
- Patient portals can really assist with ensuring you have access to your EMR health information and can participate more actively in your own care.
- The OpenNotes approach might be possible through WA’s EMR Project. (Google it. It’s very exciting!) This is quite aspirational though and may not be on the table, depending which vendor is chosen. OpenNotes will help clinicians think carefully about what they write about people, and will support the accuracy of information.
Importance of EMR Consumer Involvement
There are three levels of consumer input into training clinicians, and driving culture change:
1. Telling stories about what’s working, and what isn’t – this is effective with policy makers. Consumer stories are much more effective than clinicians providing feedback about what isn’t working for them as clinicians. Consumer stories can drive digital investment.
2. Co-designing solutions – so that the workflows centre around the patient, not the clinician. Information isn’t captured and shared for free. It always takes time and resources to share data.
3. Change management initiatives need consumers present, to make sure the tools are used in the way that helps consumers. Harry’s example of the test results not being available in the ED – it’s likely there is a portal that would allow the clinician access, but they don’t know how to use it. Consumers need to provide motivation for busy clinical staff to learn how to use the packages effectively.
Being a Digital Health Consumer/ Carer Rep:
- You know more about digital health than you think you know.
- You don’t need to understand every last technical detail – it’s important to ask naïve questions. This can prompt important critical thinking in digital health project.
- There are no stupid questions – sharing your experience is more valuable than learning “geek language” “Insist on answers in plain English. If the geeks can’t explain to you what they’re trying to do in plain English, then then you’ve probably got a program that’s not really set up for success anyway.”
- We need to think of ourselves as allies with clinicians for change, working collaboratively together. “we’re not two different actors, trying to find common ground from across the chasm, we’re actually allies working towards a common goal.”
Feeling the need to geek out? All the federal initiatives for you to google are listed below:
- Australian Digital Health Agency (ADHA) – manages My Health Record. Used to be called National Electronic Health Transition Authority (NEHTA)
- Recently released the National Healthcare Interoperability Plan
- Council for Connected Care provided strategic advice on interoperability and supporting the implementation of the National Healthcare Interoperability Plan.
- Department of Health and Aged Care – Digital Health Branch.
- Recently released the Australian Digital Health Blueprint and Action Plan
- Recently released the Aged Care and Data Digital Strategy
- Currently negotiating with states and territories on the National Health Reform Agreement
- HL7 = Health Level Seven International not-for-profit organization dedicated to supporting interoperability of healthcare data
- FHIR = Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources “an HL7 specification for Healthcare Interoperability”.
- Sparked Program – partnership of Australian Digital Health Agency, CSIRO, Department of Health and Aged Care and HL7. They are developing the Australian Core Data for Interoperability (AUCDI)
There’s a change in the air that as if to say everyone recognises that we have an opportunity, probably a once in not just a single generation, but multi generation opportunity to fundamentally transform the way our health system works
Harry Iles Mann
Want to stay in touch with the project? Just fill in The EMR Consumer Network form or email p.brennan@hconc.org.au